In an age when labeled data is the lifeblood of every machine learning workflow, auto-labeling is like having a tireless apprentice that never gets bored and seldom sleeps.
Auto Data Labels in Machine Learning: Benefits, Limits, and Use Cases
Auto Data Labels in Machine Learning: Benefits, Limits, and Use Cases
Machines label images faster than your eyes can scroll a feed. How large models learn without armies of humans clicking on every pixel? Welcome auto data labeling, a suite of techniques that let machines suggest, assign, and refine labels automatically.
In short, auto-labeling means using algorithms, often model-assisted or programmatic, to assign labels to raw data, reducing manual effort while preserving quality.
What Is Auto Data Labeling?
At its core, auto-labeling refers to machine-assisted or fully automated generation of labels or annotations for raw data. It leverages machine learning models, heuristics, and rule sets to assign category tags, bounding boxes, confidence scores, or other metadata without requiring humans to label every single example manually.
As you know, traditionally, data labeling has been done manually: human annotators read, inspect, and categorize each sample according to a guideline.
That process is very slow, expensive, and inconsistent at scale. Automated systems aim to change that dynamic.
Overall, auto-labeling uses algorithms to generate labels automatically, reducing the need for individual human annotation.
The Benefits: Why Auto-Labeling
1. Speed and Efficiency
One of the most immediate benefits of auto-labeling is obviously speed. Instead of annotators clicking through thousands or even millions of examples, automated systems can generate labels in minutes for datasets that would take weeks manually. Some model-assisted and programmatic systems can label orders of magnitude way faster than manual workflows.
2. Scalability
As datasets grow, manual labeling becomes THE bottleneck. Automated techniques, especially programmatic labeling, scale with data volume. Research showed that weak supervision techniques can generate large training sets rapidly and reproducibly, enabling domain experts to focus on labeling logic instead of individual labels.
3. Consistent Logic
We both know that humans are inconsistent, tired, distracted, and influenced by context. Auto-generated labels follow consistent logic, producing uniform annotations that help models learn more predictable patterns. This consistency is especially valuable in large-vision datasets and in repeated patterns.
4. Reduced Costs
Manual labeling scales roughly linearly with dataset size: twice the data, twice the cost. Auto-labeling systems can leverage existing models or rule sets to generate labels with minimal incremental cost.
In short, auto-labeling brings greater speed, scalability, consistency, and cost savings to the ML labeling workflow, especially as datasets grow.
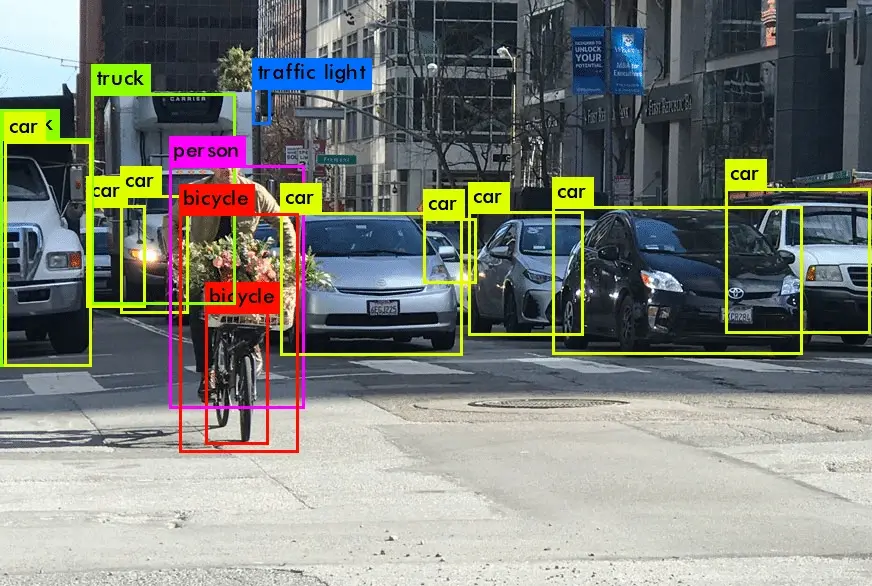
Limitations and How to Address Them: Where Auto-Labeling Struggles
1. Edge Cases and Complex Judgment
Automated labels are only as good as the underlying logic or model. If the task requires nuanced human judgment or interprets ambiguous patterns (e.g., sarcasm in text, rare objects in images), auto-labeling may mislabel examples unless humans correct or refine the logic.
At Abaka AI, we tackle this by model-assisted pre-annotation with human validation, a hybrid strategy where difficult or low-confidence examples are automatically flagged for expert review. This reduces mislabeling in complex cases and ensures that automated pipelines remain trustworthy even in edge scenarios.
2. Quality Assurance Still Required
Pure auto labeling is rarely plug-and-play. Most workflows still require a quality assurance (QA) loop where humans validate or correct low-confidence labels. This hybrid model balances efficiency with accuracy.
Here is how we address this: we build integrated QA loops into its annotation pipelines. Instead of waiting until the end of labeling, our systems sample and evaluate labels continuously, combining automated checks, inter-annotator agreement, and human review passes. Low-confidence predictions trigger human verification, ensuring labels meet accuracy thresholds before being used for training.
3. Model Bias and Confirmation
If an auto-labeler uses a model trained on biased data or limited contexts, it can propagate those biases into the labeled dataset. This is a classic case of “garbage in, garbage out”; the algorithm amplifies its own blind spots unless humans intervene.
At Abaka AI, our solution for this is to surface bias indicators early in the labeling workflow. Through systematic sampling and statistical monitoring, we flag skewed label distributions and work with annotators to adjust rules or enrich the dataset with underrepresented examples. By inserting quality checks and bias diagnostics into the loop, we reduce the chance of auto-labeling simply replicating old biases.
To sum up, auto-labeling boosts throughput but still has limitations and needs human oversight for ambiguous, subjective, or rare categories. At Abaka AI, we apply vigorous control and complex innovative solutions to address each of the issues above. Contact us to make your model an unbiased genius.
How Auto-Labeling Works: A Technical Overview
Rule-Based Techniques
Simple auto labeling uses hand-crafted rules, for example, flag all traffic signs with certain pixel patterns as “stop signs.” These are fast but brittle and only effective when the underlying logic is easily codified.
Model-Assisted Labeling
Existing models can predict labels for new data, providing suggestions that humans can confirm. This pre-annotation approach speeds up human workflows and works well when models are reasonably accurate.
Programmatic Labeling
Systems use labeling functions, small programs that encode heuristic logic, to mass-label datasets. These functions are combined and denoised to produce training data sets that closely match curated examples. This approach dramatically increases throughput and reproducibility.
Active Learning Integration
Some auto-labeling systems integrate with active learning, where the model identifies uncertain examples for human review while auto-labeling confident ones. This way, human effort is focused where it matters most.
Overall, auto-labeling encompasses rule-based, model-assisted, and programmatic systems, often combined with active learning for best effect.
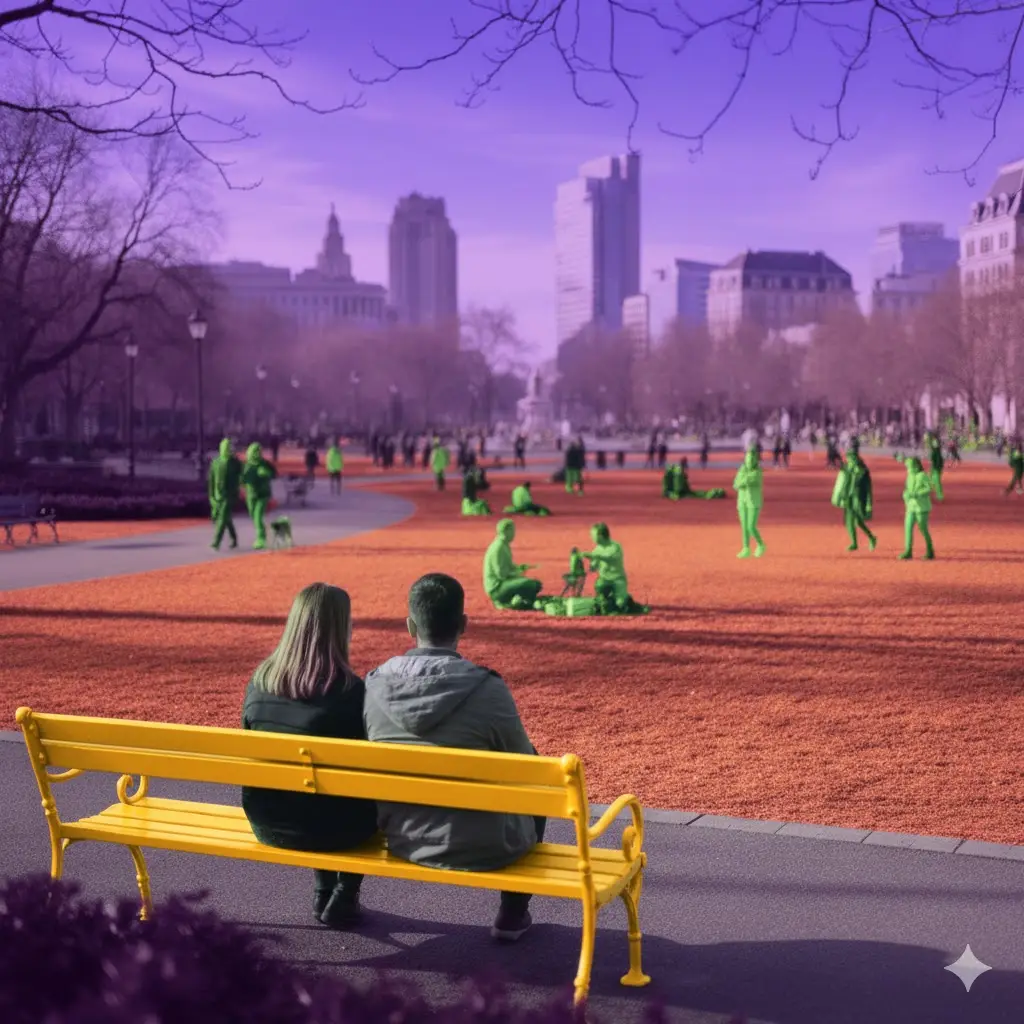

Use Cases Across Machine Learning Workflows
Auto-labeling is everywhere where machine learning needs large labeled datasets:
Computer Vision
In computer vision, bounding boxes, segmentation masks, and object classes are foundational. Auto-labeling accelerates these tasks by generating initial predictions that humans refine, especially for large image repositories.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving systems require vast amounts of labeled sensor and camera data to recognize lanes, pedestrians, and signs. Automated labeling pipelines can help meet these scale demands without prohibitively large human annotation teams.
Medical Imaging
In medical settings, auto-labeling can pre-annotate regions of interest (e.g., tumors), helping radiologists focus their expertise on what matters most. This speeds up workflows while retaining expert oversight on critical decisions.
Time Series and IoT
Sensor streams from IoT devices or industrial machinery can be auto-labeled for events like failures or anomalies, enabling predictive maintenance models with less human labeling. Although domain expertise is essential to verify, auto techniques can bootstrap large training sets.
In-Context Defect Labeling in Manufacturing
Research in display manufacturing applies automatic labeling to detect defects using in-context learning, where domain-specialized models achieve ~14 % recall improvement and maintain ~60 % coverage with auto-generated labels comparable to human-labeled data. In-context learning supports auto-label quality in industrial inspection workflows.
Overall, auto-labeling accelerates dataset creation in high-volume domains like vision, vehicles, healthcare, and IoT.
General Supervised Learning Prep
Across domains, automated labeling turns unlabeled data into structured labeled data, the “ground truth” ML models need to learn target patterns. Without labeling, supervised algorithms cannot form reliable prediction functions.
FAQs
- What is auto data labeling in simple terms?
Auto data labeling uses algorithms to assign labels to data automatically, reducing manual annotation workload and improving scalability. - How much faster is auto-labeling than manual labeling?
Automated techniques can complete labeling in minutes or hours for datasets that take weeks manually, depending on scale and task complexity. - Does auto-labeling replace humans entirely?
Not at all, most systems still need human validation and QA, especially for ambiguous cases or tasks requiring domain expertise. - What are common techniques used in auto-labeling?
Rule-based heuristics, model-assisted pre-annotation, programmatic labeling, and active learning are common approaches. - Is auto-labeling accurate enough for production ML systems?
With human review and hybrid workflows, auto-labeling provides high-quality datasets that support production-grade models, but its output should always be validated before deployment.
Further Readings:
👉AI-Powered Data Annotation Technologies: Improving Efficiency and Accuracy at Scale — How AI boosts annotation speed and quality
👉Top Annotation Tools in 2025: A Complete Guide — Compare leading platforms shaping annotation today
👉Image Annotation for Smarter Machine Learning — Best Practices for Effective Annotation
👉2025 Top Video Annotation Tools for Autonomous Vehicles — Video labeling tools for motion and scene understanding
👉2025 Top Video Annotation Tools for Healthcare — Platforms supporting medical video labeling workflows