How to Differentiate Between Real and AI-Generated Images?
💡 AI-generated images can be detected by looking for subtle artifacts and using deep learning models trained on labeled datasets. Automated classifiers now outperform human detection in most cases. For the highest accuracy at scale, use Abaka AI’s solutions that blend technology and curated data.
Understanding AI-generated vs real image datasets
A recent study published in IJIRT takes a hands-on approach using AI-generated vs real image datasets. Researchers trained a CNN model on a balanced collection of synthetic and authentic images, achieving around 91% classification accuracy. This highlights how powerful deep learning can be when paired with well-curated data.

Visual clues: anomalies and artifacts
Even high-quality AI-generated images often contain subtle inconsistencies:
- Misformed hands or extra fingers – AI models frequently struggle with anatomical correctness

- Plastic skin or eye oddities: glossy, flat, or asymmetrical eyes and skin

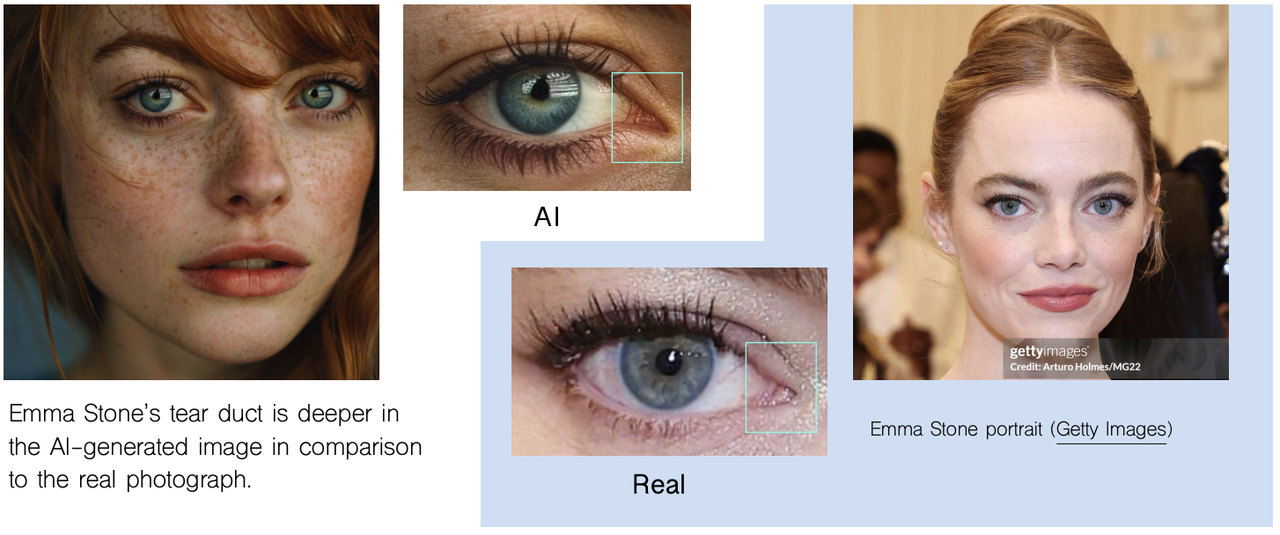
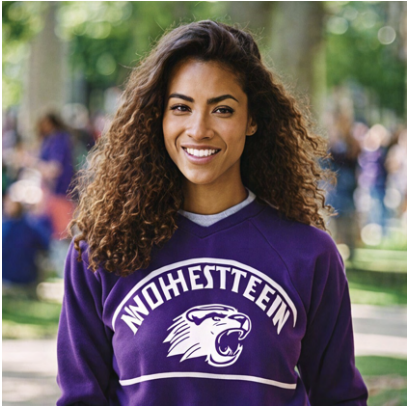
- Incoherent text – look for garbled, mirrored, or nonsensical lettering


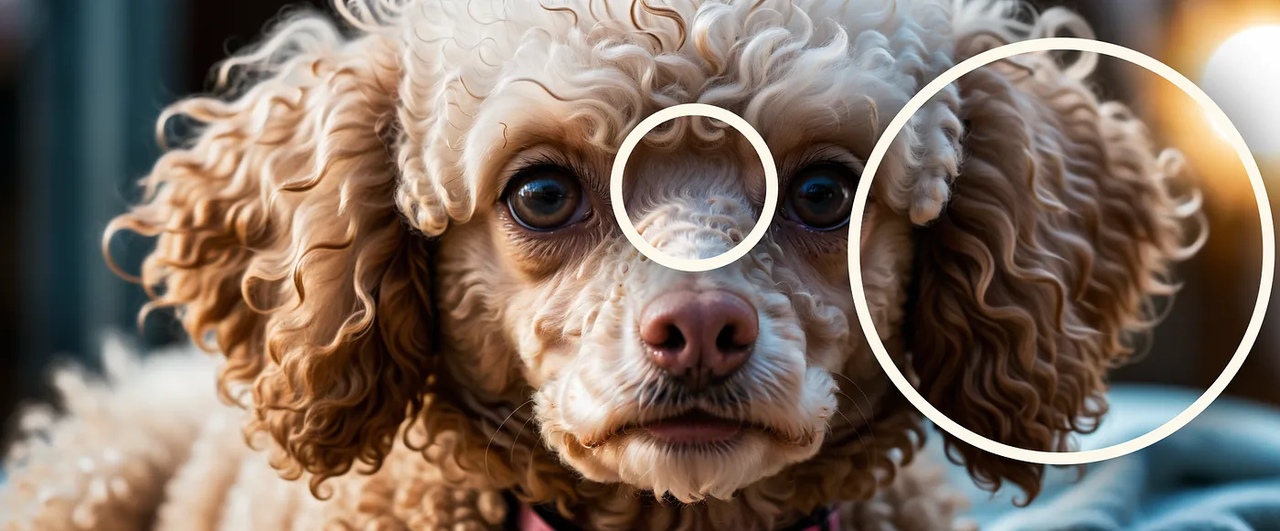
- Repetitive textures – hair, fur, foliage may show unnatural patterns

- Lighting and shadows – disparities or physically impossible projections often appear
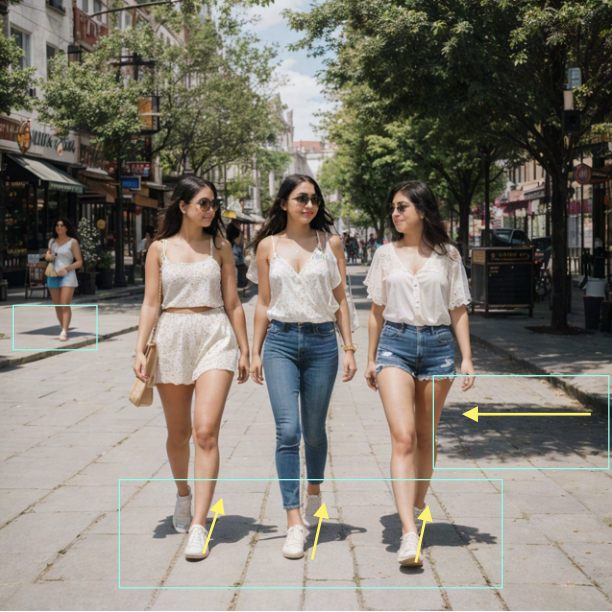

For example, in this picture, the girls' shadows fall behind them, but the tree's shadow is to its left on the sidewalk. To match the girls' shadows, the tree should be in front of its shadow. Also, the woman's shadow has sharp corners, which is odd.
- Perspective errors – misaligned lines or warped structures often give away synthetic origins
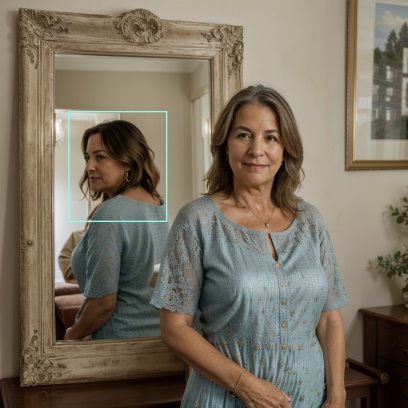
This woman is standing directly in front of the mirror, but her reflection shows her looking backwards.

Another recent guide groups these inconsistencies into five categories: anatomical, stylistic, functional, physics-based, and sociocultural—each offering clues that something’s off.
Technical Detection: Forensics & Deep Learning
When visual inspection isn’t enough, technical methods can dig deeper:
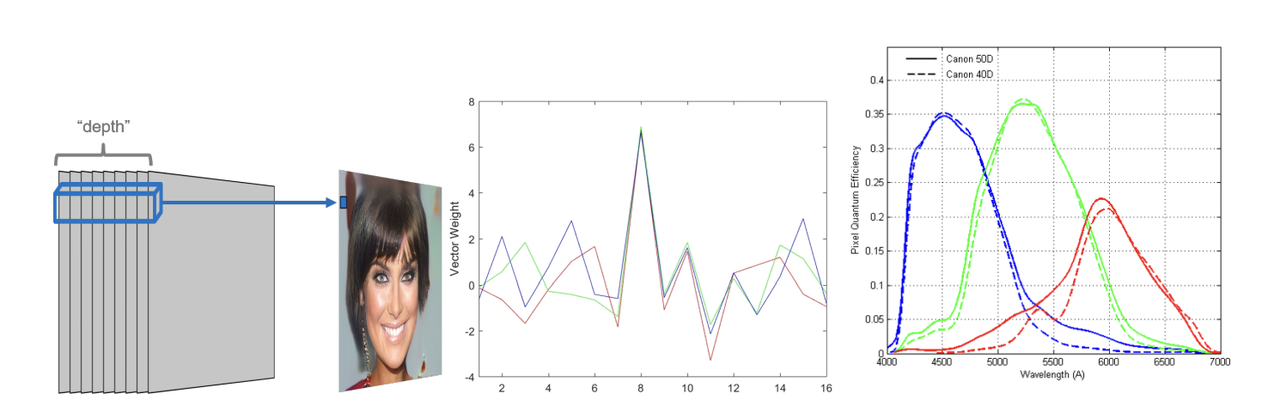
- Color distribution analysis reveals that AI-generated images (especially from GANs) tend to have certain predictable patterns that real cameras don’t.
GAN-generated images (left and center) use fixed convolutional weights to combine multiple depth layers into RGB pixels, producing consistent but artificial patterns. In contrast, real camera sensors (right) rely on color filter arrays with varying and more natural spectral responses across devices.
- Deep learning classifiers like ResNet, VGG, and DenseNet can be trained on datasets such as CIFAKE, reaching up to 98% accuracy in spotting fakes.

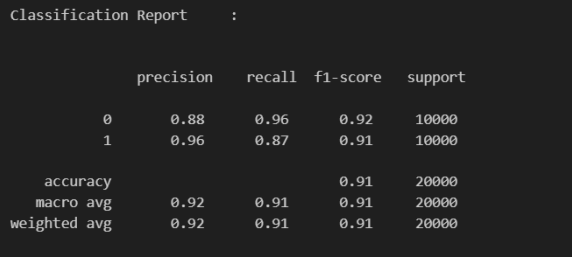
- The IJIRT model, for example, achieved:
- 91% overall accuracy
- 0.96 recall on real images
- 0.87 recall on AI-generated ones
Human vs AI: Who's Better at Spotting Fakes?
Surprisingly, humans don’t perform as well as we think. Studies show that people misclassify nearly 39% of AI-generated images. In comparison, the best AI detectors have error rates closer to 13%. This reinforces the idea that the most effective approach is combining human insight with AI assistance.
Practical checklist for image evaluation
| Checkpoint | What to look for |
|---|---|
| Hands & anatomy | Extra/missing fingers, strange limb placements |
| Text & signs | Jumbled, mirrored, pixelated text |
| Lighting & shadow | Inconsistent shadows or light angles |
| Textures & patterns | Repetitive or too-perfect textures |
| Physical coherence | Misaligned perspective or object scale |
| Color & artifacts | Unnatural color balancing or noise |
| Contextual anomalies | Odd object placements or improbable settings |
Integrating and improving detection systems
The IJIRT "Real VS AI Generated Image Detection and Classification" framework uses these steps:
- Collect a dataset of real and AI-generated images (e.g., from “This Person Does Not Exist”)
- Pre‑process (resize to 224×224, normalize, augment)
- Build CNN with convolution-pooling layers, fully connected layers, trained using Adam optimizer (Britannica Education, arXiv, IJIRT).
- Evaluate: 91 % accuracy, 0.92 F1 for real, 0.91 F1 for AI images (IJIRT).
- Deploy via an interface (e.g., Streamlit website for image uploads and classification) (IJIRT).
The study also notes areas for future improvement, such as expanding datasets, exploring newer diffusion-based models, and integrating real-time tools for content moderation on social media.
Final Thoughts
As AI tools continue to evolve, so does the art of deception. Thankfully, with the right combination of observation, technology, and critical thinking, we can stay ahead. Whether you're spotting a fake face online or verifying content for your platform, knowing what to look for—and how to leverage tools trained on AI-generated vs real image datasets—can make all the difference.
Want to boost your detection accuracy or build robust image forensics pipelines? Connect with Abaka AI to explore our data-driven solutions and level up your content verification process.