High-quality data is the fundamental catalyst for advancing AI, yet building vast, reliable, and diverse datasets is a primary bottleneck in model development. Abaka AI addresses this challenge with a distinct large-scale dataset, a meticulously curated question bank containing over one billion high-quality Q&A pairs. Sourced from authoritative materials and validated through a rigorous three-tier process of automated cleaning, multimodal verification, and expert review, our dataset provides superior "data fuel" for all stages of model training. It offers comprehensive coverage across K-12, university, and competition levels in multiple languages, with a fully structured and customizable format. By providing a massive, reliable, and diverse data foundation, our solution significantly accelerates the development cycle and enhances the performance of AI models.
Abaka 1B+ High-Quality Question Bank: Fuel for AI Revolution
Abaka's 1 Billion+ High-Quality Question Bank Ignites the "Data Fuel" Revolution
The New Paradigm: Data as the Core Engine of Scientific Discovery
Doctors use AI to screen 30,000 pathology reports. What used to require three teams and six months of work is now completed by the system in 72 hours.
When training data contains errors, even the most sophisticated algorithms will see diagnostic accuracy plummet. In the field of evidence-based science, AI is not a "magic black box" that replaces human intelligence but a "resonator" that amplifies professional value. It is reshaping the research paradigm in three ways:
- Activating Latent Knowledge: NLP is turning vast unstructured records into traceable evidence chains.
- Systematizing Serendipity: Knowledge graphs are connecting scattered findings to generate novel, reproducible insights.
- Accelerating Validation: Digital twins are simulating complex experiments, drastically shortening verification cycles.
All these transformations depend on one foundational element: high-quality, empirically sound data. As AI's inference capabilities grow, the standard for training data rises. Data is no longer a byproduct of research but the "stem cell" of production. The critical question for any organization building advanced AI is: how robust and reliable is your data?
The Solution: A 1 Billion High-Quality Question Bank Dataset for Large Models
Large models like GPT evolve through distinct training stages - Pre-Training, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Reinforcement Learning From Human Feedback (RLHF) - each demanding different types of high-quality data. The SFT stage, in particular, requires vast amounts of well-labeled, human-quality Q&A pairs to enable generalization and robust performance, a process that is traditionally slow and resource-intensive.
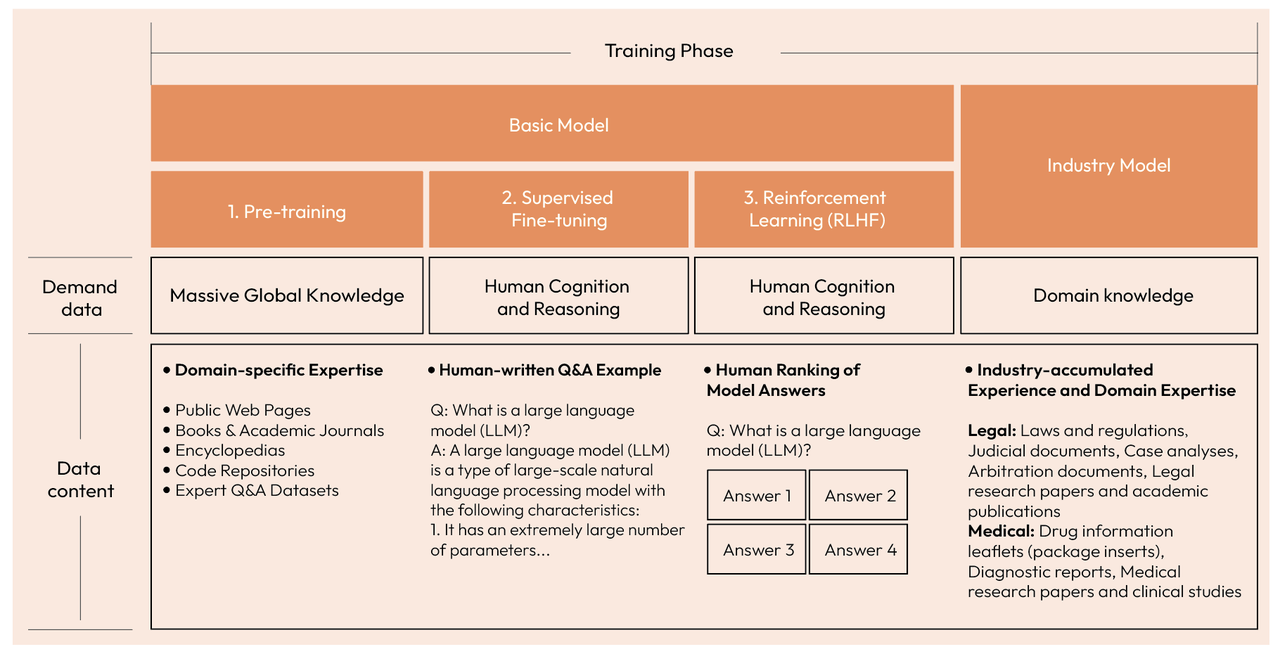
To solve this, Abaka AI has launched our 1 billion+ high-quality question bank dataset. Refined over several years and validated by numerous experts, this dataset provides our clients with the essential data needed for large model training at a lower cost and on an accelerated timeline.
A Three-Tier Quality Assurance Process
We ensure the highest data quality through a rigorous, multi-stage screening and verification process:
- Tier 1: Automated Pipeline Cleaning: An automated system cleans and validates every question for logical completeness, answer correctness, and originality, removing duplicates and handling anomalies.
- Tier 2: Multimodal Verification: We specifically process multimodal data, ensuring that any associated images are essential for problem-solving and not merely decorative or redundant screenshots of text.
- Tier 3: Subject Matter Expert (SME) Review: Data is meticulously checked by human experts. K-12 content is reviewed by senior teachers, university-level questions by PhD students, and highly specialized fields by professors, guaranteeing academic accuracy and pedagogical value.
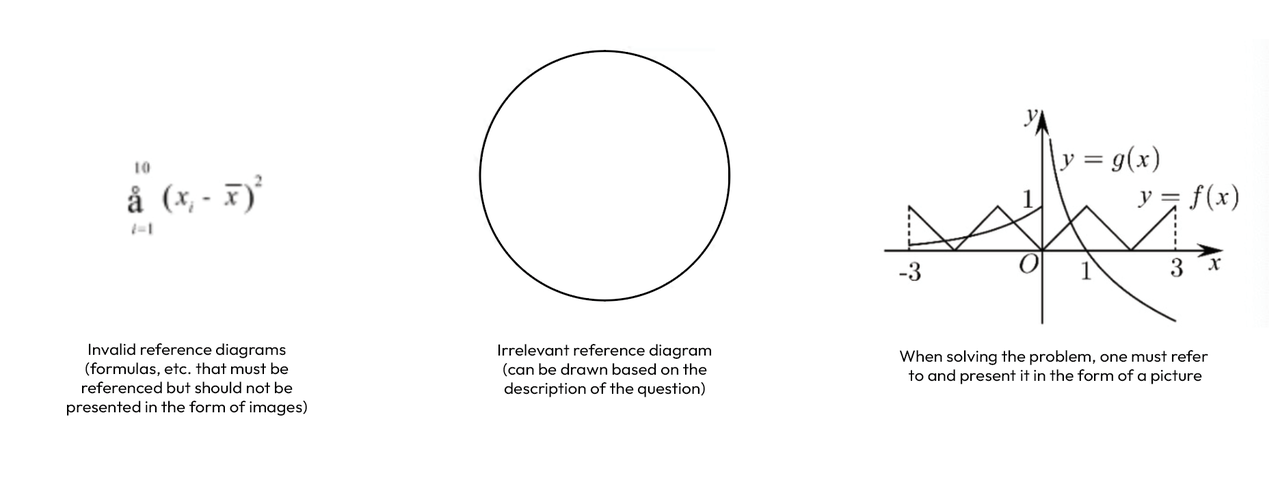
Key Features of our Dataset
The question bank dataset has been refined over several years and validated through multiple expert reviews. This dataset helps our clients meet the need for high-quality Q&A data in large model training at a lower cost and with a faster cycle.
Diversity: Comprehensive Coverage Across Subjects, Educational Stages, and Difficulty Levels
The dataset provides extensive coverage across multiple dimensions:
- K12: Over 600 million questions covering all core subjects (e.g., math, English, physics, chemistry) from primary to high school levels.
- University & Professional: Over 450 million questions, with 350+ million in STEM fields, spanning multiple languages (Chinese, English, Russian, French, Japanese).
- Competition-level: Over 1 million questions in advanced mathematics, computer science, physics, and more.
{
"id": "9c0c9330b6ae736f2e4e7cb46",
"title": "Дано $$P(-5,0)$$, точка $$Q$$ лежит на окружности $$(x-5)^{2}+y^{2}=36$$, $$M$$ — середина отрезка $$PQ$$. $$($$Ⅰ$$)$$ Найдите уравнение траектории $$C$$ точки $$M$$. $$($$Ⅱ$$)$$ Прямая $$l$$, проходящая через точку $$P$$, пересекает траекторию $$C$$ в двух точках $$A$$ и $$B$$ ($$A$$ и $$B$$ не совпадают$$)$$. $$①$$ Если $$|AB|=4$$, найдите уравнение прямой $$l$$. $$②$$ Найдите значение $$ \\overrightarrow{PA}⋅ \\overrightarrow{PB}$$.",
"option": null,
"answer": "(Ⅰ) Используя формулу координат середины отрезка и тот факт, что точка Q лежит на заданной окружности, найти уравнение траектории точки M. (Ⅱ) ① Записать уравнение прямой, проходящей через точку P, решить систему уравнений прямой и траектории C. Используя теорему Виета и формулу длины хорды, найти уравнение прямой l. ② Вычислить скалярное произведение векторов, используя их координаты и теорему Виета, чтобы найти его значение.",
"parse": "$$($$Ⅰ$$)$$ Решение: Пусть $$M(x,y)$$, тогда точка, симметричная $$P(-5,0)$$ относительно $$M$$, есть $$Q(2x+5,2y)$$. $$∵$$ Точка $$Q$$ лежит на окружности $$(x-5)^{2}+y^{2}=36$$, $$∴(2x+5-5)^{2}+(2y)^{2}=36$$, то есть $$x^{2}+y^{2}=9$$. Следовательно, уравнение траектории $$C$$ есть $$x^{2}+y^{2}=9$$.\n\n$$($$Ⅱ$$)$$\n①$$ Решение: Пусть $$A(x_{1},y_{1})$$ , $$B(x_{2},y_{2})$$. По условию, угловой коэффициент прямой $$l$$ существует, обозначим его через $$k$$, тогда уравнение прямой $$l$$ есть $$y=k(x+5)$$. Из системы уравнений $$ \\begin{cases} y=k(x+5) \\\\ x^{2}+y^{2}=9\\end{cases}$$, получаем $$(1+k^{2})x^{2}+10k^{2}x+25k^{2}-9=0$$. Из $$ \\triangle =(10k^{2})^{2}-4(1+k^{2})(25k^{2}-9) > 0$$, получаем $$- \\dfrac {3}{4} < k < \\dfrac {3}{4}$$ $$∴x_{1}+x_{2}=- \\dfrac {10k^{2}}{1+k^{2}},x_{1}x_{2}= \\dfrac {25k^{2}-9}{1+k^{2}}$$. $$∵|AB|=4$$, $$∴ \\sqrt {1+k^{2}}|x_{1}-x_{2}|=4$$, $$∴ \\sqrt {1+k^{2}}\\cdot \\sqrt {(x_{1}+x_{2})^{2}-4x_{1}x_{2}}=4$$, $$∴ \\sqrt {1+k^{2}}\\cdot \\sqrt {(- \\dfrac {10k^{2}}{1+k^{2}})^{2}- \\dfrac {4(25k^{2}-9)}{1+k^{2}}}=4$$. Решая, находим $$k=± \\dfrac {1}{2}$$. $$∴$$ Уравнение прямой $$l$$ есть $$y=± \\dfrac {1}{2}(x+5)$$, то есть $$x+2y+5=0$$ или $$x-2y+5=0$$.\n\n$$②$$ Решение: $$ \\overrightarrow{PA}=(x_1+5, y_1)$$ и $$ \\overrightarrow{PB}=(x_2+5, y_2)$$. \n$$ \\overrightarrow{PA} \\cdot \\overrightarrow{PB} = (x_1+5)(x_2+5) + y_1y_2 $$. \nТак как $$y_1=k(x_1+5)$$ и $$y_2=k(x_2+5)$$, то $$y_1y_2 = k^2(x_1+5)(x_2+5)$$. \n$$ \\overrightarrow{PA} \\cdot \\overrightarrow{PB} = (1+k^2)(x_1+5)(x_2+5) = (1+k^2)(x_1x_2 + 5(x_1+x_2) + 25) $$. \nПодставляя выражения из теоремы Виета: \n$$ = (1+k^2)\\left( \\frac{25k^2-9}{1+k^2} + 5\\left(-\\frac{10k^2}{1+k^2}\\right) + 25 \\right) $$ \n$$ = (1+k^2) \\frac{25k^2-9 - 50k^2 + 25(1+k^2)}{1+k^2} $$ \n$$ = 25k^2-9 - 50k^2 + 25 + 25k^2 = 16 $$.\n$$∴$$ Значение $$ \\overrightarrow{PA}\\cdot \\overrightarrow{PB}$$ равно $$16$$. (Это значение является степенью точки P относительно окружности C и не зависит от наклона секущей $$l$$).",
"qtype": "Задача с развернутым ответом",
"subject": "Математика/Аналитическая геометрия",
"grade": "Университет",
"has_img": false,
"image_analysis": {
"img0": {
"image_present": false
}
},
"classification": {
"major_category": "Science",
"sub_category": "Mathematics",
"subject": "Anal. Geom."
},
"correctness": {
"is_correct": true
},
"difficulty": {
"knowledge_point": "Уравнение геометрического места точек, Уравнение окружности, Уравнение прямой, Теорема Виета, Формула длины хорды, Скалярное произведение векторов, Степень точки относительно окружности",
"knowledge_level": "high school",
"educational_stage": "high school"
},
"quality": {
"logical_coherence": 5,
"educational_value": 4,
"clarity": 4
},
"question_metadata": {
"question_type": "Short Answer",
"language": "Russian",
"ai_generation_likelihood": 4
}
}
Authenticity: Reliable Sources for Questions, Answers, and Explanations
- Authoritative Sources: All questions originate from certified textbooks, official problem sets, and curated lecture notes.
- Intelligent classification: All question information (questions, answers, explanations, knowledge points, and diagrams) is stored in a fully structured way. A key feature is our proprietary, hierarchical
classificationsystem. This refined taxonomy, validated by both AI and human experts, enables precise, cross-domain, high-quality data screening and application. - Standardized Formulas: All scientific and mathematical expressions and formulas are encoded in standard LaTeX, ensuring seamless integration and error-free parsing.
{
"id": "dcb705347f19e67c20de8a97",
"title": "A certain metal ion $M^{n+}$ reacts with ammonia to form the complex $[M(NH_3)_6]^{n+}$. If the magnetic moment of the complex is zero and the electronic configuration of the metal ion is $d^6$, determine the position of the metal ion in the periodic table and explain the reasoning.",
"option": null,
"answer": "Iron",
"parse": "Based on the information provided, the metal ion has an electronic configuration of $d^6$, and the formed complex has a magnetic moment of zero. This indicates that all unpaired electrons are paired. For a $d^6$ electronic configuration, in an octahedral field, the magnetic moment can only be zero when a low-spin state is formed, meaning all electrons occupy the $t_{2g}$ orbitals and are fully paired. Therefore, the metal ion should belong to Group VIII. A common metal ion with a $d^6$ configuration and capable of forming a low-spin state is iron. Iron's position in the periodic table is in the fourth period, Group VIII.",
"qtype": "Short Answer",
"subject": "Chemistry/Chemistry",
"grade": "University",
"has_img": false,
"image_analysis": {
"img0": {
"image_present": false
}
},
"classification": {
"major_category": "Science",
"sub_category": "Chemistry",
"subject": "Inorg. Chem."
},
"correctness": {
"is_correct": true
},
"difficulty": {
"knowledge_point": "Coordination chemistry, Crystal field theory, Electronic configuration, Magnetic moment, Periodic table",
"knowledge_level": "high school",
"educational_stage": "university"
},
"quality": {
"logical_coherence": 4,
"educational_value": 4,
"clarity": 4
},
"question_metadata": {
"question_type": "Short Answer",
"language": "English",
"ai_generation_likelihood": 4
}
}
Accuracy: Deduplication, Standardization, and Expert Verification
Accuracy is guaranteed through a multi-layered validation process:
- Semantic Deduplication: An AI-driven process eliminates redundant questions based on deep semantic similarity, ensuring the purity of the database.
- Standardized Architecture: All data adheres to a strict, unified JSON schema, providing a cornerstone of consistency and quality.
- Two-Stage Correctness Verification: Answers and explanations undergo a robust "double-checking" process: initial screening by AI models, followed by meticulous review from human subject matter experts.
correctnessfield serves as the final adjudicator, accurately identifying and forcibly eliminating all “problematic questions”. This process systematically identifies and removes any problematic questions, including those with content errors, logical loopholes, or conceptual flaws.
{
"id": "6807164f991513c1ae30f45a",
"title": "The source of carbon dioxide (CO_{2}$) is from which of the following processes?",
"option": [
"A. Gas obtained after desulfurization and conversion of semi-water gas",
"B. Waste gas produced by lime kiln combustion",
"C. Direct collection of industrial waste gas",
"D. Direct combustion of natural gas"
],
"answer": "A",
"parse": "In the Hou's combined soda-making process, semi-water gas is treated with desulfurization and conversion to obtain conversion gas containing CO_{2} as raw material. This process meets the soda-making requirements and also solves the issue of decarbonizing the raw material gas for ammonia synthesis. Option B refers to the CO_{2} source in the Solvay process, Option C does not specify a clear industrial waste gas source and does not match the process description, and Option D mentions CO_{2} from natural gas combustion without desulfurization or other preprocessing steps, all of which do not meet the question's intent.",
"qtype": "Single Choice",
"subject": "Chemistry/Industrial Chemistry",
"grade": "University",
"has_img": false,
"image_analysis": {
"img0": {
"image_present": false
}
},
"classification": {
"major_category": "Engineering",
"sub_category": "Chemical Engineering and Technology",
"subject": "Mass Trans. & Sep. Process in Chem. Eng."
},
"correctness": {
"is_correct": false,
"error_type": "Wrong Answer"
},
"difficulty": {
"knowledge_point": "Industrial Chemistry, CO2 sources, Haber-Bosch process, Solvay process",
"knowledge_level": "high school",
"educational_stage": "university"
},
"quality": {
"logical_coherence": 3,
"educational_value": 4,
"clarity": 2
},
"question_metadata": {
"question_type": "Single Choice",
"language": "English",
"ai_generation_likelihood": 4
}
}
Customization: Flexible Question Bank Structure, Tailored for Specific Subjects and Languages
The dataset is designed for adaptability to specific training needs:
- The data schema is fully customizable, allowing fields to be added, modified, or removed.
- Support for niche subjects and languages can be tailored for specialized model training.
- Questions in the form of QA pairs can be used for RL-verified construction.
- Measurement to filter the question bank data sets with high probability of making mistakes in certain large models and empower targeted training to improve.
{
"id": "67ff4799a366742fe5edf95b",
"title": "In the nine-point difference scheme of the Poisson equation, the order of the error term $R_{i,k}^*$ is:",
"option": [
"A. $O(h^2)$",
"B. $O(h^4)$",
"C. $O(h^6)$",
"D. $O(h^8)$"
],
"answer": "C",
"parse": "According to the derivation of the nine-point difference scheme, the estimation of the error term $R_{i,k}^*$ includes a term of $h^6$, so its order is $O(h^6)$.",
"qtype": "Single Choice",
"subject": "Mathematics/Numerical Analysis",
"grade": "University",
"has_img": false,
"image_analysis": {
"img0": {
"image_present": false
}
},
"classification": {
"major_category": "Science",
"sub_category": "Mathematics",
"subject": "Num. Anal."
},
"correctness": {
"is_correct": true
},
"difficulty": {
"knowledge_point": "Poisson equation, nine-point difference scheme, error term, order of accuracy, numerical analysis",
"knowledge_level": "university",
"educational_stage": "university"
},
"quality": {
"logical_coherence": 4,
"educational_value": 3,
"clarity": 4
},
"question_metadata": {
"question_type": "Single Choice",
"language": "English",
"ai_generation_likelihood": 4
}
}
Beyond the Question Bank: AI for Science (AI4S)
Recognizing that advanced AI for Science (AI4S) models require more than just Q&A data, Abaka AI has also constructed two supplementary databases of academic papers and textbooks.
This non-question bank data is essential for training models in vertical domains where deep, contextual knowledge from primary sources is paramount. Together, these datasets provide a holistic data solution to meet the diverse requirements of the AI4S research landscape.
The era of data-driven AI is here, and the quality of your training data will define your success. Abaka AI's 1 Billion+ question dataset, alongside our extensive academic and textbook databases, provides the meticulously curated, verified, and structured "data fuel" you need to power the next generation of AI models. Whether you are fine-tuning a large language model, building a specialized AI for science, or require a custom dataset tailored to your unique domain, our team is ready to help.
Contact Abaka AI today to discuss your project, request a data sample, and discover how we can accelerate your development cycle and unlock new levels of model performance. Let's build the future of AI, together.